Introduction
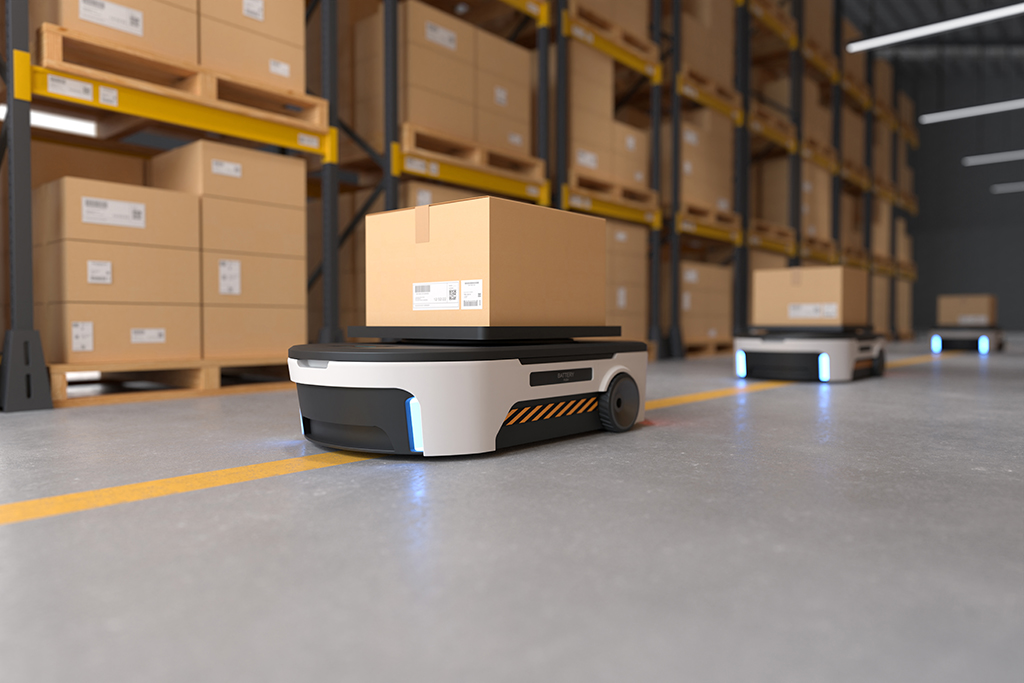
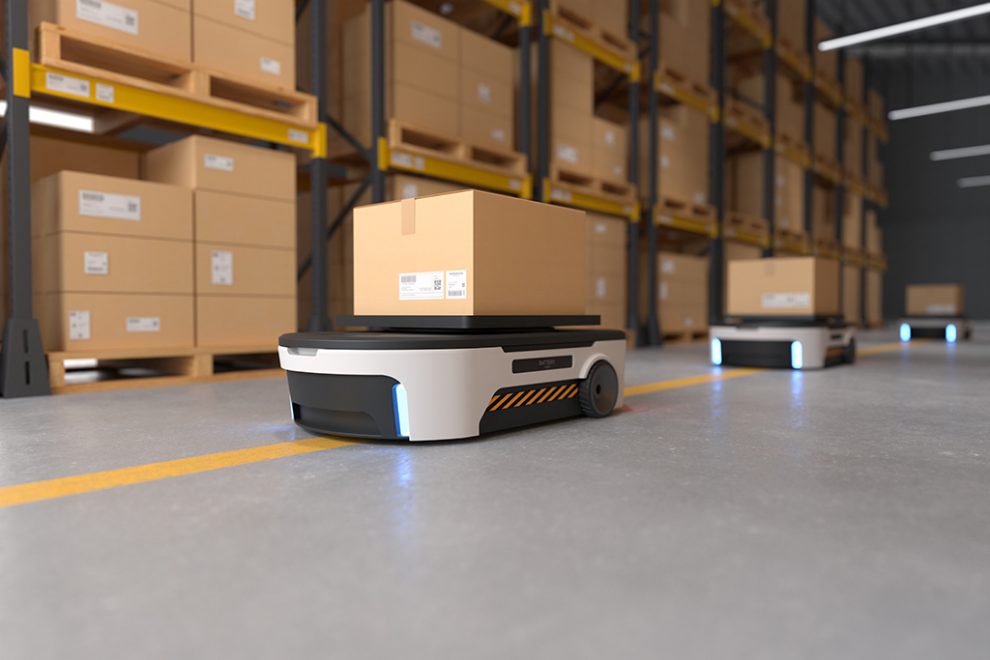
Inventory management is a critical aspect of warehouse operations, ensuring efficient stock control, accurate order fulfillment, and optimized supply chain management. With the advancement of technology, automation has emerged as a game-changer in streamlining inventory management processes. By leveraging automation, warehouses can improve accuracy, increase efficiency, and reduce costs. In this article, we will explore the benefits of automating inventory management in warehouses, supported by existing technologies and real-world examples.
I. The Need for Automated Inventory Management
1.1 Challenges in Traditional Inventory Management
Traditional inventory management methods, relying on manual processes and paper-based systems, are prone to human errors, delays, and inefficiencies. These challenges can lead to inaccurate stock counts, misplaced items, stockouts, and order fulfillment delays.
1.2 Benefits of Automation in Inventory Management
Automating inventory management in warehouses brings a range of benefits. It enables real-time visibility of inventory levels, improves accuracy in stock counts, enhances order accuracy and fulfillment speed, reduces labor costs, and provides valuable data for demand forecasting and supply chain optimization.
1.3 Real-World Example: Amazon Fulfillment Centers
Amazon, a global leader in e-commerce, has revolutionized inventory management through automation in its fulfillment centers. The use of robotic systems for inventory storage, retrieval, and movement has significantly increased efficiency and accuracy. Automated systems, such as Amazon’s Kiva robots, work collaboratively with human workers to ensure efficient order fulfillment and inventory management.
II. Technologies Enabling Automated Inventory Management
2.1 Barcode and RFID Technologies
Barcode and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technologies play a crucial role in automated inventory management. Barcodes and RFID tags are attached to products, enabling quick and accurate identification and tracking. Scanning devices and RFID readers capture data, allowing for real-time updates of inventory levels and locations.
2.2 Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) integrate various technologies and provide a centralized platform for managing inventory. WMS software tracks inventory, facilitates order processing, optimizes storage space, and generates reports for inventory analysis and decision-making.
2.3 Real-World Example: DHL’s Smart Warehouse
DHL, a global logistics company, has implemented automated inventory management systems in its warehouses. Through the use of barcode scanning, RFID technology, and advanced WMS software, DHL achieves accurate inventory tracking, efficient order processing, and improved customer service. Their smart warehouses demonstrate how automation enhances inventory management in large-scale logistics operations.
III. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Inventory Management
3.1 AI-Powered Demand Forecasting
Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms can analyze historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant factors to forecast demand accurately. AI-driven demand forecasting helps warehouses optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize overstocking.
3.2 Predictive Analytics for Supply Chain Optimization
Predictive analytics, powered by AI, enables warehouses to anticipate future demand, optimize supply chain operations, and reduce lead times. By analyzing data from multiple sources, including inventory levels, production capacity, and transportation, warehouses can make informed decisions to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
3.3 Real-World Example: Walmart’s AI-Powered Inventory Management
Walmart, one of the world’s largest retailers, has embraced AI in its inventory management processes. By leveraging machine learning and predictive analytics, Walmart optimizes inventory levels, reduces waste, and improves product availability. Walmart’s success in using AI demonstrates the transformative potential of the technology in inventory management.
Conclusion
Automating inventory management in warehouses brings numerous benefits, enabling real-time visibility, improving accuracy, enhancing order fulfillment, and optimizing supply chain operations. Real-world examples from industry leaders such as Amazon, DHL, and Walmart showcase the transformative impact of automation in inventory management. By leveraging technologies like barcode and RFID, warehouse management systems, and AI-driven analytics, warehouses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and deliver better customer service. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of automation and AI will further enhance inventory management capabilities, enabling warehouses to meet the increasing demands of modern supply chains efficiently.